VARICOSE VEINS
Varicose Veins Disease appears enlarged, swollen, and twisted in blue, red, or flesh-colors, typically occurring in the legs and feet. This common condition affects millions of people worldwide.
CAUSES OF VARICOSE VEINS
Varicose Veins develop when weakened or damage valves cause blood to flow backward and pool in the veins. As This leads to veins becoming enlarged, twisted, and often painful. Also, several risk factors contribute to the development of varicose veins:
- Age (the risk increases with age)
- Gender (women are more likely to develop them)
- Family history
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged standing or sitting
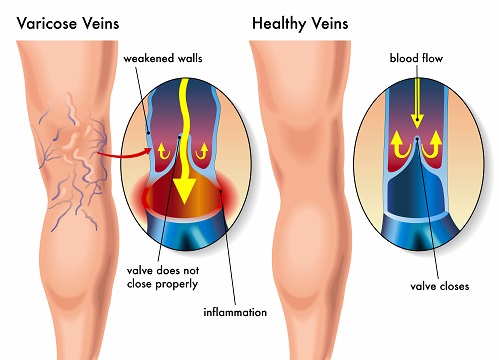
SYMPTOMS OF VARICOSE VEINS
- Initially, you notice twisted veins that appear blue or purple.
- Moreover, you experience swollen, achy, or heavy-feeling legs.
- Additionally, you feel pain, burning, or itching in the affected area.
- Finally, you see skin discoloration or ulceration around the affected area.
DIAGNOSING AND TREATING VARICOSE VEINS
At first, physicians diagnose this medical condition through a physical exam and a review of your medical history. In some cases, they may use imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
For instance, Varicosa Veins can be treated with various outpatient, minimally invasive procedures, or through hospital-based surgeries, depending on the severity of the condition.
Outpatient, Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Endovenous Laser Ablation Therapy (EVLT): This minimally invasive procedure uses laser energy to close the affected vein. A small incision is made, and a laser fiber is inserted into the vein. The laser heats the vein, causing it to collapse and seal shut. Blood reroutes to healthy veins, and the treated vein is reabsorbed by the body.
1. Immediate Post-Procedure Care:
– Compression Stockings: Wear them to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
– Walking: Walk for 10-15 minutes immediately to promote circulation and prevent blood clots.
– Pain Management: For mild discomfort, use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen.
2. Short-Term Recovery:
– Physical Activity: Resume daily activities within 24-48 hours, but avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting for a week.
– Follow-Up: A follow-up ultrasound within a week or two ensures the vein has closed properly.
3. Long-Term Recovery:
– Results: Symptoms improve in a few days, but full reabsorption of the vein may take weeks.
– Monitoring: Regular check-ups monitor treated veins and detect new varicose veins early.
Sclerotherapy: This minimally invasive procedure injects a solution into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade. It treats small to medium varicose veins.
1. Immediate Post-Procedure Care:
– Compression: Wear compression stockings or bandages for several days to enhance results.
– Avoid Sun Exposure: Protect treated areas from sunlight to prevent dark spots.
2. Short-Term Recovery:
– Activity: Resume normal activities the same day, but avoid strenuous activities, hot baths, and saunas for a few days.
– Pain Management: Use cold packs and over-the-counter pain relievers for mild discomfort or bruising.
3. Long-Term Recovery:
– Results: Veins gradually fade, with full results in weeks to months. Multiple sessions may be needed for optimal results.
– Monitoring: Regular check-ups assess treatment success and manage potential complications.
Ablation of superficial veins with Microfoam
Varicose vein therapy uses an injectable foam that closes diseased veins. Micofoam is a minimally invasive option, and in clinical trials only 4.0% of patients reported pain at the injection site. No cuts or stitches are required, and the procedure typically takes under an hour. Most patients see results after just one session.
Ablation of superficial veins with Radio Frequency
The Ablation System uses radiofrequency (RF) energy, a method that has been a trusted treatment for chronic venous disease (CVD) for more than two decades.
- Minimally invasive, performed as an outpatient procedure
- Requires only a small catheter entry point
- Often considered the preferred treatment by physicians
Hospital-Based Surgeries:
Phlebectomy: Surgeons make small incisions in the affected area and use a specialized instrument to remove the affected vein. Typically, they use this procedure to treat larger varicose veins that minimally invasive treatments cannot address.
High Ligation and Stripping of Varicose Veins: Surgeons make a small incision in the affected area, tie off the vein, and then remove it. This procedure is generally used for larger veins that minimally invasive methods cannot treat.
The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and, importantly, the individual needs of the patient. In addition, our team of experienced vascular specialists at Messner Vascular Institute can work with you to determine, accordingly, the best course of treatment for your varicose veins. Furthermore, our goal is to provide you with the highest quality of care and, ultimately, help you achieve optimal vascular health.
