DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the leg. Consequently, the clot can interfere with normal blood flow, potentially leading to complications such as pulmonary embolism.
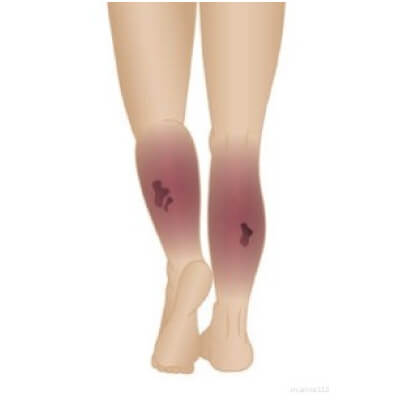
SYMPTOMS OF DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
- Swelling in the affected leg.
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, especially when standing or walking.
- Warmth and redness in the affected area.
- Enlarged veins near the surface of the skin.
- Leg fatigue or heaviness.
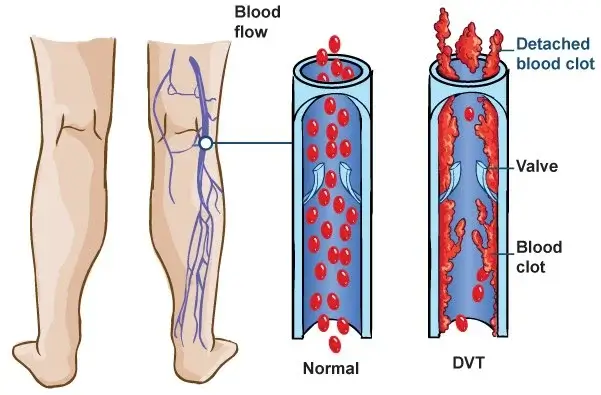
COMMON CAUSES OF DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)
Several factors can increase your risk of developing DVT, including:
- For instance, prolonged periods of inactivity: Sitting or standing for long periods can increase your risk of developing DVT.
- Recent surgery or hospitalization: Surgery and hospitalization can increase the risk of blood clots forming.
- In addition, injury to a vein can increase the risk of clot formation.
- Cancer and chemotherapy: Some cancers and cancer treatments can increase the risk of blood clots forming.
- In particular, hormone therapy and birth control pills: These can increase the risk of blood clots in some people.
- Consequently, pregnancy increases the risk of blood clots forming.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR DVT:
Treatment for DVT typically involves blood thinning medications to prevent the clot from getting bigger and to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism.
Alternatively, other treatment options may include:
- Compression stockings: These help to reduce swelling in the affected leg and improve blood flow.
- Catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT): This is a minimally invasive procedure that involves using a catheter to deliver medication directly to the clot, thus dissolving it.
- Vena cava filter: In some cases, a small filter may be placed in the inferior vena cava, the large vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart, to prevent blood clots from traveling to the lungs.
Finally, if you suspect you may have DVT, it is important to seek medical attention right away. The experienced of Doctor Gregory Messner, D.O. FACOS vascular specialists at Messner Vascular Institute can work with you to determine the best course of treatment for your condition and help you achieve optimal vascular health.
