PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASES (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Diseases (PAD), is a common condition where plaque buildup in the arteries restricts blood flow, primarily affecting the legs. It can also impact other arteries in the body, including those in the kidneys, abdomen, feet, and arms. PAD is often caused by atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits and cholesterol narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to tissues.
CAUSES OF PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASES (PAD)
Is caused by atherosclerosis, a build-up of plaque (fatty deposits and cholesterol) on the walls of the arteries. Over time, the arteries can become so narrow that it is difficult for blood to flow through and bring oxygen to the muscles, tissue and organs. Clots can form when plaque breaks off and enters the bloodstream.
Risk factors include:
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
- High blood pressure and high cholesterol levels
- Heart disease such as Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Smoking
- Family history of heart or vascular disease
- Overweight (body mass index over 30)
- Lack of exercise and sedentary lifestyle
- Over 70 years old (or over 50 if you also smoke and/or have diabetes)
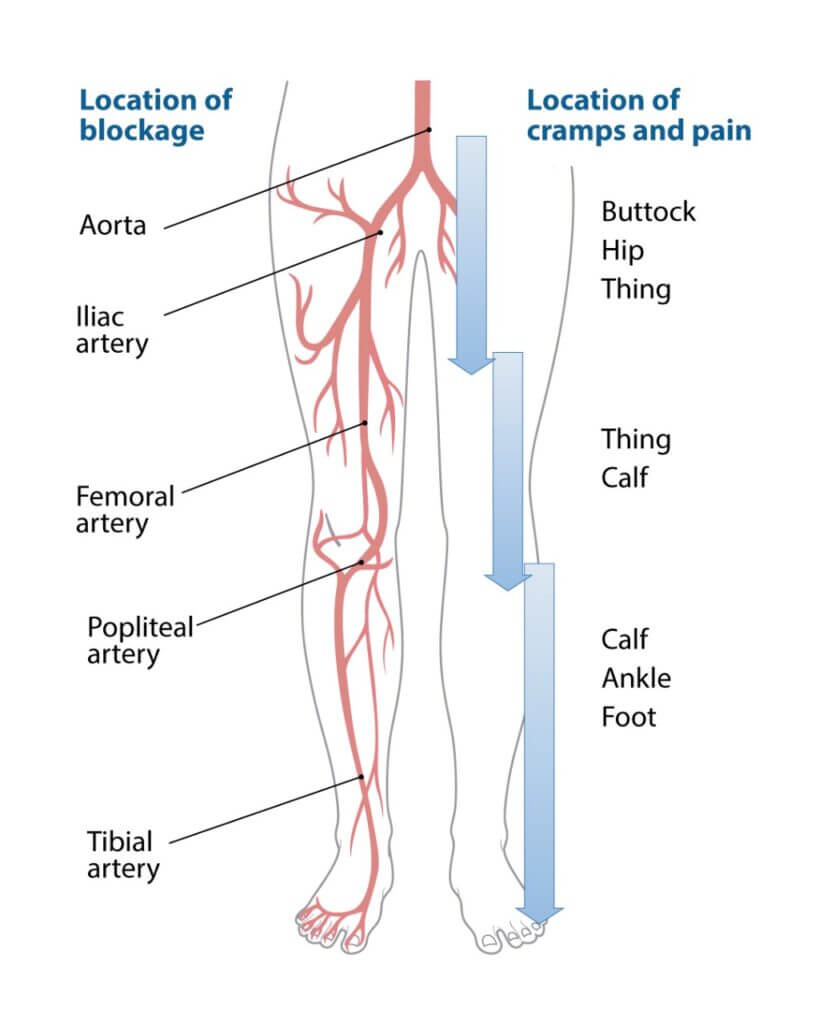
SYMPTOMS OF PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASES (PAD)
Initially, many individuals with PAD might not experience any symptoms; however, as the condition progresses, several symptoms may begin to appear. First, you may notice pain or cramping in your legs, especially during walking or exercise. Additionally, as the disease advances, your legs might feel unusually cold or numb. Moreover, there could be a tingling sensation that disturbs your sleep at night.
Furthermore, the skin on your legs may start to discolor, becoming either pale or bluish. If left unchecked, sores or wounds on your feet may develop, which, unfortunately, won’t heal properly due to the poor blood circulation. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor any cuts or swelling on your feet closely. If you notice that wounds are slow to heal or not healing at all, it’s crucial to consult your doctor as soon as possible.
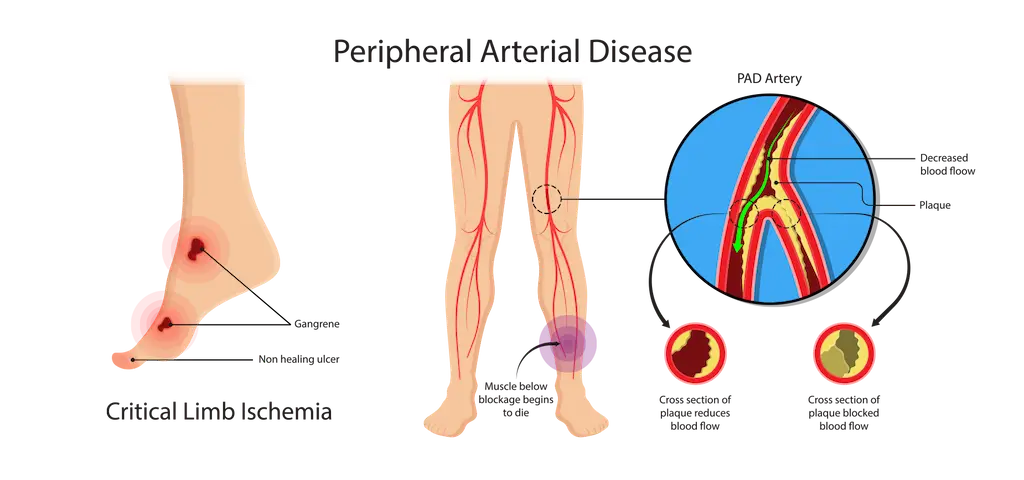
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR PHERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASES (PAD)
Initially, diagnosis PAD typically involves checking the pulse in your feet and an ankle-brachial index test. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, medications, and, in severe cases, minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting to restore blood flow and prevent complications like amputation.
ASYMPTOMATIC PAD
Patients with asymptomatic PAD should receive a comprehensive program of guideline-directed management and therapy (GDMT), which includes a structured exercise and lifestyle modification program, to reduce cardiovascular events, such as stroke or heart attack, and improve function. Suggested lifestyle modifications would include lowering blood pressure and cholesterol, losing weight and stopping smoking. Medications are customized to each patient’s individual risk factors, such as diabetes, high blood pressure or hyperlipidemia.
SYMPTOMATIC PAD
Patients who have experienced symptoms of Peripheral Artery Diseases (PAD) and have an ABI of less than 0.90 are diagnosed with one of two conditions:
1. Claudication: Claudication occurs when patients experience cramping and pain in their legs during exercise due to obstructed arteries reducing blood flow. The pain, known as intermittent claudication, fades when the patient rests. If untreated, it can persist and limit activity and quality of life. A customized care plan includes a supervised exercise program to relieve claudication symptoms and enhance life quality. Revascularization becomes necessary when lifestyle-limiting claudication does not improve with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT).
2. Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI): CLI arises from severe arterial obstruction that significantly reduces blood flow to extremities, causing constant pain and ulcers on the feet. Unlike intermittent claudication, CLI pain does not subside with rest. To prevent amputation, surgical or endovascular revascularization is recommended. This treatment aims to restore blood flow, alleviate ischemic pain, heal wounds, and preserve limb function, minimizing tissue loss.
In addition, if PAD progresses, it could develop into Acute Limb Ischemia (ALI) which is seen as a medical emergency. Patients with ALI must be treated rapidly because the longer the symptoms are present, the greater the risk of limb damage.
ENDOVASCULAR REVASCULARIZATION TECHNOLOGY
(click the procedure above to learn more)
LEARND MORE ABOUT DIABETES AND BLOOD SUGAR
Diabetes significantly impacts Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) by elevating blood sugar levels, which contribute to atherosclerosis. Elevated glucose levels from diabetes lead to the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries, causing them to narrow and restrict blood flow. This condition reduces oxygen and nutrients to tissues, exacerbating PAD symptoms and increasing the risk of severe cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and strokes. Managing blood sugar effectively is crucial in preventing and controlling PAD. For optimal cardiovascular health and PAD management, understanding the link between diabetes and blood sugar levels is essential.
Amputations and invasive surgeries for PAD are now rare, thanks to endovascular (minimally invasive) procedures. Dr. Messner, who specializes in these techniques, has performed over 6,000 procedures, including laser atherectomy and angioplasty with stenting.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Procedures For Peripheral Artery Diseases:
- Same-Day Return Home: Patients undergo procedures on an outpatient basis, allowing them to return home the same day without hospitalization.
- Faster Recovery with Less Pain: Minimal incisions and reduced anesthesia result in quicker healing and less pain, so patients resume normal activities with minimal downtime.
- Better Overall Results: Advanced technology enables Dr. Messner to precisely address and resolve vascular issues effectively.
- Increased Safety: Endovascular procedures involve fewer risks of infection and complications due to the absence of large incisions compared to traditional surgery.
- Amputation Prevention: These minimally invasive procedures often restore blood flow to the feet and legs, reducing the risk of amputation.
