Gregory N. Messner, DO, Ali Azizzadeh, MD, T. Tam Huynh, MD, Anthony L. Estrera, MD, Eyal E. Porat, MD, and Hazim J. Safi, MD
- PMID: 16429916
- PMCID: PMC1351843
Free PMC article
Abstract
We present the case of a 71-year-old woman who had benign, symptomatic, superior vena cava syndrome that was treated with open surgical bypass using the superficial femoral vein. The patient had an uneventful hospital course and experienced relief of her symptoms. We conclude that the superficial femoral vein is an acceptable bypass conduit for open surgical management of superior vena cava syndrome.
Keywords: Blood vessel prosthesis, femoral vein/transplantation, superior vena cava syndrome/diagnosis/etiology/surgery, vascular patency
Superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome can present in a variety of ways, depending on the severity of the obstruction as well as the cause. Complete obstruction can cause a patient’s condition to deteriorate rapidly, whereas obstruction due to benign disease may be indolent. Most cases are caused by malignancy. Benign cases are increasing, due in large part to iatrogenic injuries from central venous catheters and transvenous pacemakers.1 As a result, management strategies vary from anticoagulation and medical management to stenting or surgical bypass.
Case Report
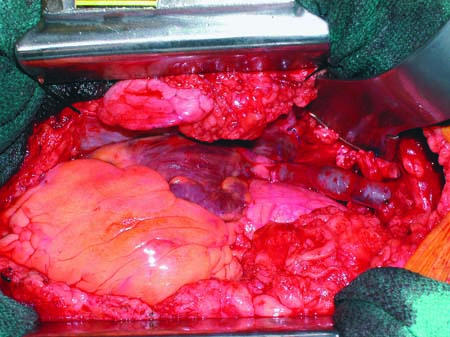
A 71-year-old woman presented at our institution with shortness of breath, dizziness, and lower-extremity and facial swelling. She had a history of placement of multiple central venous catheters due to congestive heart failure. Chest radiography and duplex ultrasonography of the legs and the carotid arteries revealed no abnormality. Computed tomography of the chest revealed the diagnosis of superior vena cava syndrome with a severe obstruction. The patient underwent a bypass from the brachiocephalic vein to the right atrium with use of the superficial femoral vein (Fig. 1). The operation was performed through a median sternotomy. Intraoperative pathology specimens showed no malignancy. The patient tolerated the procedure well and was discharged on postoperative day 10. She experienced remarkable improvement in her respiratory symptoms. There was minimal lower extremity swelling secondary to vein harvesting.
At 8-month follow-up, the patient was ambulatory and asymptomatic; echocardiography showed that the reconstructed superior vena cava was widely patent.
Discussion
Surgical bypass of the SVC was first reported by Klassen and associates in 1951 with use of an autologous femoral vein.2 Since then, few reports in the English-language medical literature have described the use of an autologous femoral vein to bypass the superior vena cava.3–5 Using the methods described by Wells and colleagues5 and surveying the venous system preoperatively with duplex ultrasonography, we have found that the superficial femoral vein can be removed quickly and the size match is acceptable. The results of superficial femoral vein harvest were also reported by Wells and co-authors, who found only mild signs of chronic venous insufficiency in fewer than 33% of patients.5
The use of the composite vein graft was first described by Benvenuto and co-authors in 1962.6 Doty and colleagues7 adopted this technique and showed a long-term patency rate of 87.5% at 10.9 years; they also reported a patent graft in 1 patient at 24 years.8 Kalra and coworkers9 described a primary patency rate of 53% and an assisted primary patency rate of 68% at 5 years with use of spiral saphenous, superficial femoral, allograft, and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) grafts. However, the secondary patency rate of vein grafts (spiral saphenous and superficial femoral) at 5 years was 90%.9 The main concern with this technique is the possibility of thrombosis due to multiple long suture lines; however, this has not been shown.
The treatment of nonmalignant SVC obstruction remains surgical, while percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting are effective to maintain secondary patency of vein grafts. Smayra and associates10 reported on 13 patients stented for SVC syndrome who had a primary patency rate of 40% at 17 months. Another report, by Kalra and coworkers,9 described 3 patients who were stented for benign disease: 2 underwent multiple repeat interventions, and 1 patient chose to undergo spiral saphenous vein grafting at another institution rather than undergo another endovascular intervention.
The primary patency rate of stenting in malignancies varies from 75% to 85%, with secondary patency rates of 85% to 91%.11–14 The reported complication rate for stenting is around 19%.13,14 In a series of 30 patients, Smayra’s group reported a complication rate of only 7%, with 1 immediate death after stent placement.10 These results show that surgical intervention in malignancy may be useful as well. In a study by Doty and associates,8 spiral vein grafting was performed in 6 patients who had malignant disease. None experienced a recurrence of SVC obstruction, and 4 patients survived 1 year or longer after surgery.
Surgical treatment of SVC syndrome that results from benign disease is effective, with excellent long-term results. The use of an autologous vein, whether it be for a superficial femoral vein graft or a spiral saphenous vein graft, provides better results than can be attained with stenting or with PTFE grafts. Endovascular intervention is effective at maintaining secondary patency of grafts; however, the use of endovascular techniques in the short term is associated with frequent repeat interventions. In our patient, an 8-month follow-up examination revealed her to be ambulatory and asymptomatic. Echocardiography showed that the reconstructed superior vena cava was widely patent.
Footnotes
Address for reprints: Gregory N. Messner, DO, Texas Heart Institute, MC 3-258, P.O. Box 20345, Houston, TX 77225-0345
E-mail: ten.epacsten@gergssem
References
Articles from Texas Heart Institute Journal are provided here courtesy of Texas Heart Institute
Superior vena caval bypass using the superficial femoral vein is a critical surgical procedure used to treat superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS), a condition caused by the obstruction or narrowing of the superior vena cava, which can severely impede blood flow to the heart. This condition is often seen in patients with cancer, especially lung cancer or lymphoma, but can also occur due to blood clots or other vascular disorders. The procedure is particularly valuable when traditional treatments, like stenting or radiation, are not effective or viable.
In this procedure, surgeons use the superficial femoral vein, a vein located in the thigh, to bypass the blocked portion of the superior vena cava. The superficial femoral vein is chosen because of its accessibility, size, and the fact that it can be safely harvested without causing significant complications or loss of function. Once the vein is harvested, it is grafted to form a bypass, allowing blood to flow freely from the upper body to the heart, bypassing the obstruction.
The superior vena caval bypass using the superficial femoral vein provides patients with significant relief from the symptoms of SVCS, which can include swelling of the face, neck, and upper limbs, as well as difficulty breathing and swallowing. The bypass helps restore normal venous circulation, improving the patient’s quality of life and overall prognosis.
Advances in surgical techniques and postoperative care have made this procedure safer and more effective. By utilizing the superficial femoral vein for bypass, surgeons can offer a viable solution for patients suffering from severe venous obstruction, improving venous return and mitigating the risks associated with untreated superior vena cava syndrome. This procedure is a valuable tool in managing complex vascular issues and enhancing patient outcomes.